How To Find the Best Psychiatrist in Mumbai For Depression?
How To Find the Best Psychiatrist in Mumbai For Depression? Read Post »

M.A. in Psychology (Clinical)
Clinical Psychologist & Psychotherapist
Community Out-reach Manager
Experience: 6 Years
Expertise: Anxiety, Depression, Schizophrenia, Addiction, Trauma, ADHD, Intellectual Disability, Autism.
Age range: Toddler to Adults
Speaks: English, Hindi, Gujarati and Kutchi
Mode of Sessions: Online / In Person
Schools of Therapy: Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT), Behavioural Therapy (BT), Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET), Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT)
Ms. Nidhi Karia offers her expertise to individuals of all ages facing diverse psychological concerns. Her clientele ranges from children with behavioural issues to adults dealing with severe mental health disorders. She has significant experience working with substance abuse and addiction at a reputable rehabilitation centre, and has also contributed her skills to the Institution of Exceptional Children and Advitya. Known for her friendly and empathetic demeanour, Ms. Karia is dedicated to her clients’ well-being. She firmly believes in helping individuals recognize their unique qualities and is committed to fostering the development of their distinctive strengths. Additionally, her unwavering dedication and personalised approach make her a trusted figure in her field.
(M.A., PURSUING PHD)
CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST & PSYCHOTHERAPIST ADVISOR & MENTOR
Ms. Neha Bhansali is a clinical psychologist, psychotherapist and a senior faculty at the Post-Graduate Department of Psychology at Maniben Nanavati women’s college- teaching M.A. psychology (counselling and clinical specialization). She has rich experience in teaching, mentoring as well as a practitioner in therapy for over 12 years.
She is a certified Arts Based Therapy Practitioner and has completed a Master Trainer course in Life Skills from Indian Association of Life Skills Education. She is also a certified CBT therapist from Swasti Institute in collaboration with Beck Institute, USA. Her Primary work is with children, adolescent and young adult population. With her experience and expertise she consults as a Senior Advisor to the team of Reflect Within.

(M.D. PSYCHIATRY)
Psychiatrist & Psychotherapist Advisor & Mentor
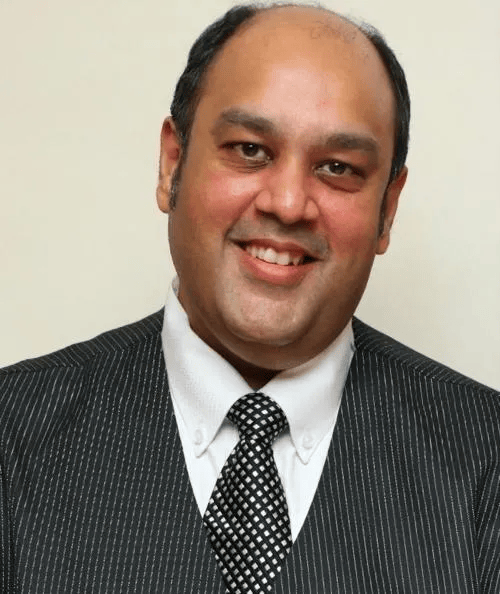
Dr. Avinash De Sousa is a senior consultant psychiatrist and psychotherapist at L.T.M.G.H. (Sion Hospital ), H.N. Reliance foundation, Goenka Group of Schools and also proud Founder Trustee of DeSousa Foundation. He is a visiting faculty at several recognized institutes and medical colleges in Mumbai. He is also the current president of Bombay Psychiatric Society (BPS). He has been contributing to the field of mental health for the past 25+ years.
He is one of the most renowned psychiatrists of the city. He has over 800 publications in national and international journals. He is one of the few psychiatrists who in addition to a psychiatry degree has an MBA in Human Resource Development, a Masters in Psychotherapy and Counselling and an MPhil in Psychology. He is also the editor of a journal called Indian Journal of Mental Health. He is an excellent mentor as well as an inspiration to the students & young professionals and is an Advisor and consulting psychiatrist at Reflect Within.

M.O. Th,
Occupational Therapist
Experience: 3 Years
Expertise: ADL training, ADHD, Autism, Sensory Processing Disorders, Cerebral Palsy, Intellectual Disability, Developmental delays, Parkinson, Dementia, Stroke, MND, Multiple Sclerosis, Psychosis.
Age range: Toddler to Geriatric
Speaks: English and Hindi
Mode of Sessions: In person
Schools of Therapy: Sensory Integration Therapy, Play Therapy, Physical Therapy, Neurodevelopmental Therapy.
Ms. Srishti Dhanania is a dedicated Occupational Therapist with experience across various age groups and clinical settings. She specializes in providing individualized treatment for developmental delays, sensory processing challenges (ASD), and mental health conditions like Psychosis.
Holding a Master’s in Mental Health and Psychosocial Rehabilitation, she also works with a diverse population, helping clients build functional skills for a balanced, fulfilling life. Her experience spans hospitals, residential care, and community programs, allowing her to tailor interventions to different environments.
She is passionate about promoting holistic well-being and believes in integrating creative therapeutic techniques to enhance engagement in therapy. Srishti emphasizes a strengths-based approach, empowering clients to navigate challenges with confidence. Through her work, she strives to foster meaningful participation in daily activities, ensuring her clients lead independent and enriched lives.

M.A., (Counselling Psychology),
Sr. Psychologist
Experience: 10 Years
Expertise: Anxiety, Depression, Grief and Loss, Self-esteem, Body Image Issues, Relationship counseling, Gender & sexuality related concerns.
Age range: Adolescent, Young Adults and Adults
Speaks: English, Hindi and Gujarati
Mode of Sessions: In person / Online
Schools of Therapy: Humanistic, REBT, CBT, Internal Family Systems, Narrative, Transactional Analysis
Ms. Bansri Mehta has practiced in various capacities, including schools and hospitals, and has a deep passion for teaching psychology. In her therapeutic practice, she adopts an integrative approach, drawing from diverse tools and techniques across therapeutic styles to best meet her clients’ unique needs. She is committed to encouraging, empowering, and equipping her clients with effective and healthy coping strategies.
With a warm, empathetic, and non-judgmental presence, Ms. Bansri provides a safe space for her clients to explore their thoughts and emotions. Her work is rooted in compassion, genuineness, and the belief that every individual has the strength to overcome challenges. Guided by the grounding words of C.S. Lewis, “Courage, dear heart,” she supports her clients in navigating life’s complexities with resilience and confidence.

M.A. in Clinical Psychology
Sr. Clinical Psychologist & Psychotherapist
Business Development Manager
Experience: 12 Years
Expertise: Parenting Coach, Marital Issues, Anxiety, Depression, Addiction, ADHD.
Age range: Adults and Geriatric
Speaks: English, Hindi and Marathi
Mode of Sessions: Online
Schools of Therapy: Schools of Therapy: Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT), Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), Solution Focused Brief Therapy (SFBT)
Ms. Kalyani Govekar Joshi has over 12 years of experience across diverse fields, including corporates, de-addiction centers, schools, mental health centers, geriatric counseling, and child/adolescent counseling. She specializes in de-addiction, anxiety, depression, marital, and interpersonal issues.
In her corporate experience, Ms. Kalyani has worked extensively with a Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) on recruitment processes, serving on interview panels, conducting group discussions, behavioural analysis, and situational assessments. She has collaborated with the thermal power plant, IT, and fintech industries, delivering webinars and workshops on mental well-being, work-life integration, and leadership development. Her role at Reflect Within has been instrumental in expanding corporate wellness programs, bringing a holistic approach to mental health.
Additionally, Ms. Kalyani’s work in the educational sector includes heading a resource room where she led assessments, diagnoses, and teacher training programs. Her comprehensive experience enables her to bring a well-rounded perspective to mental health and well-being across different age groups and sectors.
Ms. Kasturi Roy
Location: Kandivali (E)
Days: Friday and Saturday
Time: 11:00 AM to 08:00 PM
Ms. Urja Shah
Location: Kandivali (E)
Days: Monday to Saturday
Time: 11:00 AM to 08:00 PM
Ms. Nidhi Karia
Location: Kandivali (E)
Days: Tuesday, Thursday and Friday
Time: 11:00 AM to 8:00 PM
Ms. Vinanthi Hegde
Location: Kandivali (E)
Days: Monday to Saturday
Time: 11:00 AM to 8:00 PM
Ms. Nidhi Karia
Location: Kandivali (W)
Days: Monday, Wednesday and Saturday
Time: 11:00 AM to 08:00 PM
Dr. Ameet Thanky
Location: Kandivali (W)
Days: Tuesday and Thrusday
Time: 05:00 PM to 7.00 PM

M.A. in Psychology and Diploma in Remediation
Psychologist and Remedial Educator
Lead, School Mental Health Co-ordinator
Experience: 3 Years
Expertise: ADHD, Autism Spectrum Disorder, Intellectual Disability, Learning Disability, Social Anxiety & Separation Anxiety.
Speaks: English, Hindi, Gujarati
Mode of Sessions: In Person
Schools of Therapy: Eclectic and child-centred approach, Behavioural Therapy (BT), Play Therapy, Remedial Strategies
Ms. Urja Shah is a trained mental health professional, specialising in the assessment and providing intervention for children and adolescents. She has previously worked with the Institution of Exceptional Children, Vallabhdas Dagara Indian Society for the Mentally Challenged, and Sion Hospital. She is currently associated with multiple schools, providing psychological services and mental health support.
She is compassionate and empathetic, and has a genuine desire to help children who are struggling with emotional, behavioural, or developmental issues, overcome their challenges and reach their full potential. She values the saying by Haim Ginott that – “Children are like wet cement. Whatever falls on them makes an impression.”

M.B.B.S, M.D. Psychiatry
Psychiatrist & Sexologist
Experience: 9 Years
Expertise: Mood Disorders, Personality Disorders, Sexual Disorders, Psychosis, Delusions, Schizophrenia, Addiction, Substance Abuse, Suicidal Thoughts, Neurodevelopmental Disorders, OCD, Anxiety Disorders.
Age range: Children to Adults
Speaks: English, Hindi and Gujarati
Mode of Sessions: Online
Dr. Dhruv J. Parmar is a Consultant Psychiatrist, Sexologist, De-addiction and Insomnia specialist. In Addition to his Degree in Psychiatry from LTMMC, Sion, Mumbai, he has done his fellowship in Psychosexual Medicine from JSS University, Mysuru, Advanced course in management of Addictive Disorders from NIMHANS, Bengaluru and the World Psychiatric Association’s course on management of Insomnia. Has been a speaker in various National and International Conferences. Has numerous publications in National and International Journals. Apart from treating the core Psychiatric issues, he specialises in management of Psychosexual issues, Addictive Disorders and Insomnia. He strongly believes in de-stigmatising mental health issues and that the key to a healthy body is a healthy mind. He lives by his motto, ‘It’s ok to not be ok’ and makes sure it’s a key in his treatment plan.

M.A., MPhil RCI No- RCI NO. A71974
Sr. Clinical Psychologist & Psychotherapist
Experience: 13 Years
Expertise: Anxiety, Depression, Schizophrenia, Addiction, Suicidal Ideation, Self-Harm, ADHD.
Age range: Adolescents to Adults
Speaks: English, Hindi and Marathi
Mode of Sessions: Online
Schools of Therapy: Eclectic approach with humanistic care, Cognitive Behavioural Therapy and Cultural Sensitivity.
Mr. Swapnil Bhopi’s enthusiasm, persistence, and mindfulness have helped him achieve great heights in benefiting individuals and society at large. He has worked at prestigious hospitals, including the Sir JJ Group of Hospitals, and has conducted various workshops on topics such as stress management, suicide prevention, and de-addiction awareness at government and private organizations. He has also been interviewed on these topics by various newspapers and social media platforms. Additionally, he has experience as a resource person for Continuing Nursing Education (CNE) by the Maharashtra Nursing Council and has appeared on various reality shows. His comprehensive approach and dedication to his work have made significant impacts in his field.

B.sc in Microbiology, PG in Nutrition and Food
Nutritionist
Experience: 15 Years
Expertise: Nutritional deficiencies in children and adults with mental health conditions.
Age range: Toddler to Adults
Speaks: English, Hindi and Gujarati
Mode of Sessions: Online / In Person
Mrs. Khushbu Mehta is a valedictorian post graduate in Nutrition and Food Technology from SNDT college. A thorough understanding in child and general population nutrition is expressed through her 15 years of practice into the field of Nutrition and graduation from Microbiology. She is currently pursuing her postgraduate diploma in Nutritional psychiatry from Centre for Nutrition and Dietetics Studies. She specifically deals with children with special needs, developmental delays and adults struggling with their mental health due to their eating habits, mental health concerns and having poor esteem due to weight gain or weight loss. She defines her purpose of being a nutritionist for a greater cause: the process of saving people from health myths or faulty food habits by discerning science-based information on health and equipping them with it. Her catchphrase is ‘Get your food right, your mind will nourish on its own.’

B.O.Th., M.O. Th
Occupational Therapist
Experience: 7 Years
Expertise: ADHD, Autism, Cerebral Palsy, and Developmental delays, Parkinson, Dementia, Stroke, MND, Multiple Sclerosis.
Speaks: English, Hindi, Gujarati, Marathi
Mode of Sessions: Offline / In Person
Dr. Helly Shroff currently serves as an Occupational Therapist at Reflect Within. She holds a Bachelor’s degree (B.O.TH) and a Master’s degree (Neuro) in Occupational Therapy from KEM Hospital. With over five years of experience in the field, she has worked at prestigious institutions such as Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital, the Multiple Sclerosis Society, the Haemophilia Society, and Disha Counselling Centre. Her expertise spans a wide range of cases, including ADHD, Autism, Cerebral Palsy, and Developmental delays.
Dr. Shroff is a compassionate Occupational Therapist dedicated to providing the highest quality patient care. She possesses the ability to develop treatment programs that enhance a client’s capacity to carry out daily activities and occupations independently, thereby boosting their confidence. Additionally, she specialises in addressing Adult Neurological conditions, including Stroke Rehabilitation, Parkinson’s disease, Neuropathies, Brain injuries, Dementia, MNDs (Motor Neuron Diseases), and Multiple Sclerosis.

(B.P.Th) Clinical Physiotherapist (Pediatric)
Physiotherapist
Experience: 15 Years
Expertise: Cerebral Palsy, Bell’s Palsy, Hydrocephalus, Microcephalus, Spina Bifida.
Speaks: English, Hindi, Gujarati and Marathi
Mode of Sessions: In Person
Dr. Ameet Thanky has demonstrated success in facilitating treatment for both outpatients/ inpatients by his fine diagnostic skills, in-depth patient evaluation and developing a treatment plan in order to achieve patient mobility. He majorly deals with patients having Cerebral Palsy cases needing corrective surgery, pre-op and post-op rehabilitation, Syndromic Cases with developmental delay, babies with prolonged NICU stay, premature babies, Bell’s Palsy – facial paralysis, bladder rehabilitation and a lot more.
He is a skilled medical care professional with wholehearted dedication towards patient care and willingness to learn & keep abreast of new developments in the medical field.
His main motto since he started his practice is – “To always be patient centric. Giving them an optimistic reality check so that an acceptance develops towards the illness and planning a suitable therapy program to achieve a desirable therapy goal. Also framing home ex’s program to maintain the progress. Busting the myths related to the illness.”

M.B.B.S, M.D. Psychiatry, DNB, MIPS
Psychiatrist
Experience: 9 Years
Expertise: Mood Disorders, Personality Disorders, Neurodevelopmental Disorders, Behavior Issues, Schizophrenia, Addiction, Substance Abuse, Suicidal Thoughts, OCD, Anxiety Disorders, Psychosis, Delusions.
Age range: Children to Adults
Speaks: English, Hindi, Marathi
Mode of Sessions: In Person
Dr. Rohit Deshmukh holds an M.D. in Psychiatry, which he earned from the renowned Grant Government Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals in Mumbai. His extensive medical training and clinical exposure have equipped him with the expertise to address a wide spectrum of mental health conditions, thanks to his comprehensive experience gained during his tenure at Sir J.J. Hospital. In addition to this, he has also dedicated his professional efforts to the Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry at Nair Hospital.
His approach to mental health is guided by a profound belief: he views mental illness not merely as a medical condition but as a product of an individual’s life experiences and the circumstances that surround them. This perspective enables him to gain a deep understanding of the underlying factors contributing to a person’s mental health challenges, allowing him to take a comprehensive and holistic approach to their treatment and well-being.

M.A., REBT Certified
Sr. Counselling Psychologist & Psychotherapist
Experience: 15 Years
Expertise: Marital Issues, Anxiety, Depression, Grief.
Age range: Adolescents to Adults
Speaks: English, Hindi, Gujarati and Marathi
Mode of Sessions: In Person
Schools of Therapy: Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT), Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), Solution Focused Brief Therapy (SFBT)
Mrs. Sneha Rao Parmar is a counselling psychologist and a family therapist with over 15 years of experience. She has wide expertise in, namely, couple, family counselling & marital therapy, adult counselling that focuses on stress management and anxiety issues and working with children and adolescents with special needs, assessing children with academic difficulties, developmental delays, behavioural problems, and counselling parents. Additionally, she has been a guest lecturer at various organisations such as SOPAN, SSRVM, Arya Vidya Mandir and Mary Immaculate as a visiting faculty. She also has conducted CRE workshops with teachers across Maharashtra for RCI licenced psychologists. She always says, “If it doesn’t challenge you, it doesn’t change you.”

M.A. in Applied Clinical Psychology
Consultant Clinical Psychologist & Psychotherapist
Internship Supervisor
Experience: 8 Years
Expertise: PTSD, OCD, Schizophrenia, Eating Disorder, Adult ADHD, Marital and Relationship Issues, Personality Disorders, Gender & sexuality related concerns.
Age range: Adolescents to Adults
Speaks: English, Hindi and Bengali
Mode of Sessions: Online / In person
Schools of Therapy: Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT), Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), Art Based Therapy, Behavioural Therapy (BT), Acceptance and Commitment Based Therapy (ACT), Solution Focused Brief Therapy (SFBT)
Ms. Kasturi Roy is a consulting clinical psychologist and psychotherapist at Reflect Within. Her therapeutic approach is characterised by its versatility and adaptability. She employs a range of evidence-based therapeutic modalities to tailor her treatment to the unique needs of each individual. She is known for her effectiveness in helping individuals identify and modify unhelpful thought patterns and behaviours, fostering positive change in their lives. Ms. Roy provides her clients with a diverse range of tools to explore and navigate their inner worlds, fostering self-discovery and healing.

M.sc in Psychology
Lead, Assessment and Evaluation
Experience: 4 Years
Expertise: OCD, Anxiety, Depression, Trichotillomania, Eating Disorder, Social Anxiety, Separation Anxiety.
Age Range: Toddler, Adolescents and Young Adults
Speaks: English, Hindi, Kannada
Mode of Sessions: Online / In Person
Schools of Therapy- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy(CBT), Rational Emotive Behavioural Therapy (REBT) Gestalt , Art based approach, Somatic Training
Ms. Vinanthi Hegde is an empathetic person and active listener. She is a passionate researcher, having written, presented, and published various research papers, and has also worked under IIT Roorkee. Her research spans diverse topics in psychology, contributing valuable insights to the field. She has experience working with NGOs like Shraddhanand Mahilashram and Manav Seva Sangh, addressing legal cases such as rape, sexual abuse, and unwed mothers, and has also worked with hospitals like Dimhans and Sion Hospital. She strongly believes in the saying by Soren Kierkegaard, “Life is not a problem to be solved but a reality to be experienced.”
WhatsApp us
